Fat Transfer
What is Fat Transfer?
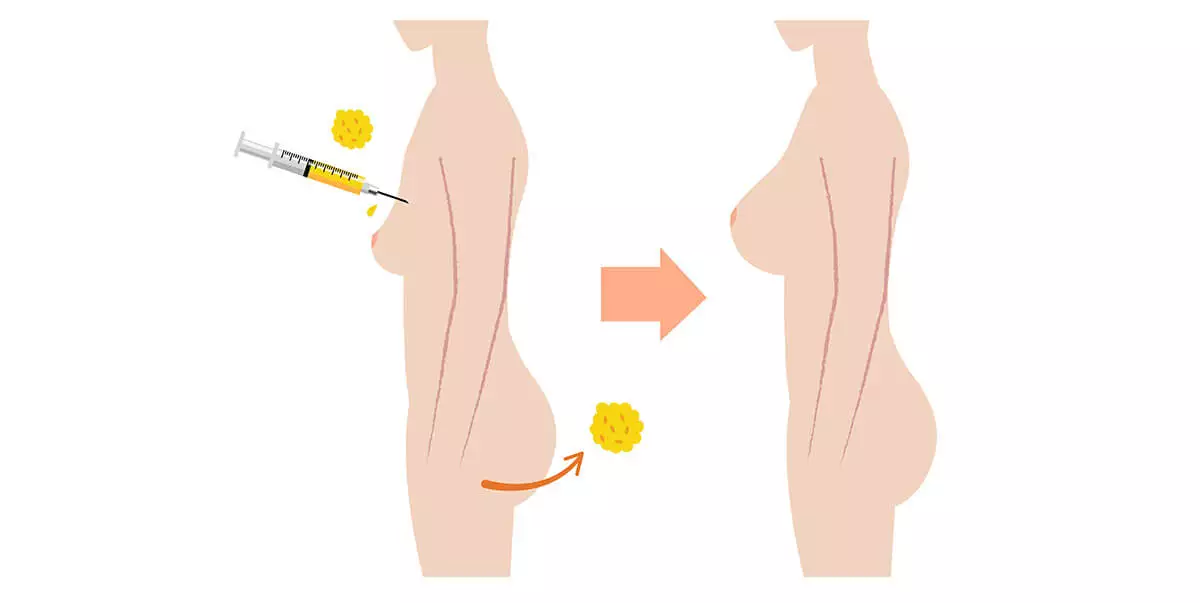
Fat Transfer, also known as Fat Injection, Fat Grafting, Lipomodelling, and Adipose Tissue Transfer, aims to increase the volume of a targeted area through transferring excess fat from the patient’s body to a targeted area such as the face, under the lower eyelids, hips, and the buttocks. Fat Injection is performed frequently and provides natural looking long-term results that are often permanent.
Why is Fat Transfer performed?
Fat Transfer allows a targeted area to increase in volume through the existing fat cells in the body, without the use of any kind of implants. Fat Transfer’s results are expected to be long term unlike and fillers, making Fat Transfer preferable over them for the treatment of facial collapses and wrinkles. Fat Transfer is also the preferred treatment for hiding surgical scars and irregularities in the body contour.
What are the conditions for Fat Transfer?
Fat Transfer requires Liposuction to be initially performed, so to qualify for Fat Transfer the patient must qualify for Liposuction. Requirements of Liposuction include:
- Being able to undergo local or general anesthesia.
- Being within 20 - 25 lbs (10 kg) of the patient’s ideal weight.
Which surgeries involve Fat Transfer?
Some operations are composed of just Fat Transfer and are named different according to the target area:
- Butt: Brazilian Butt Lift
- Lips: Lip Augmentation
- Breasts: Breast Augmentation
Fat Transfer can also be combined with any other Aesthetic surgery, but is most commonly combined with Face Lift to fill existing lines and pits on the face, such as deep acne and scars.
What Are The Things To Be Considered Before Fat Transfer?
Before the surgery, the patient should:
- Be at the hospital a day before their surgery for the pre operative tests to be performed.
- Stop smoking and consuming alcohol at least 2 weeks before the surgery to alleviate the risk of a blood clot.
- Avoid medication containing aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) for two weeks before and after surgery. These medications may increase the risk of internal bleeding. Patients should confirm each medication and supplement they wish to take with their Patient Coordinator.
- Stop taking Multivitamin supplements 7 days prior to the surgery, and if it contains vitamin K should not be used for 30 days following the surgery.
- Stop taking oral contraceptives 30 days before the surgery.
Before the surgery, the donor areas and the areas to be transferred for Fat Transfer are decided, and corresponding drawings are made.
How is Fat Transfer performed?
General or local anesthesia is administered and then small incisions are made at the donor area. Fat Transfer is done in 3 steps: Fat collection, cleaning and transport, and insertion. The Fat Cells are removed with the chosen type of Liposuction through a small cannula. The extracted fat is then washed, cleaned, and filtered if needed. A special thin cannula is then inserted into the target area through tiny incisions. The fat cells are injected through the cannula into the target area.The process is repeated until the desired body contour is achieved. Some surgeons recommend massaging the area where the procedure is performed for more effective results.
Fat Transfer, on average, takes 1 to 4 hours.
What are The Things To Be Considered After Fat Transfer?
After the surgery, pain, swelling, and bruising are to be expected and will usually subside within a few weeks. Additionally tube drains might be placed at the end of the surgery to prevent the accumulation of blood or other body fluids. After the surgery, the patients are recommended to:
- Minimize exposure to sunlight and heat, as they might exacerbate swelling.
- Avoid strenuous physical activity for two weeks after surgery.
It might take 2 to 3 weeks for the swelling to go down, therefore the results of the surgery will not be visible until then.
When the process is performed successfully, the results are often permanent; however, some areas may need adjustment depending on the patient's demand or need.
What Are The Risks of Fat Transfer?
Risks of Fat Transfer include, but are not limited to:
- Fluid accumulation near the skin, Seroma
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Infection
- Swelling
- Poor wound healing
- Scarring
- Changes in skin sensation
- Damage to nerves, blood vessels, and muscles.
- Adverse reaction to anesthesia
