Roux En Y Gastric Bypass
What is Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
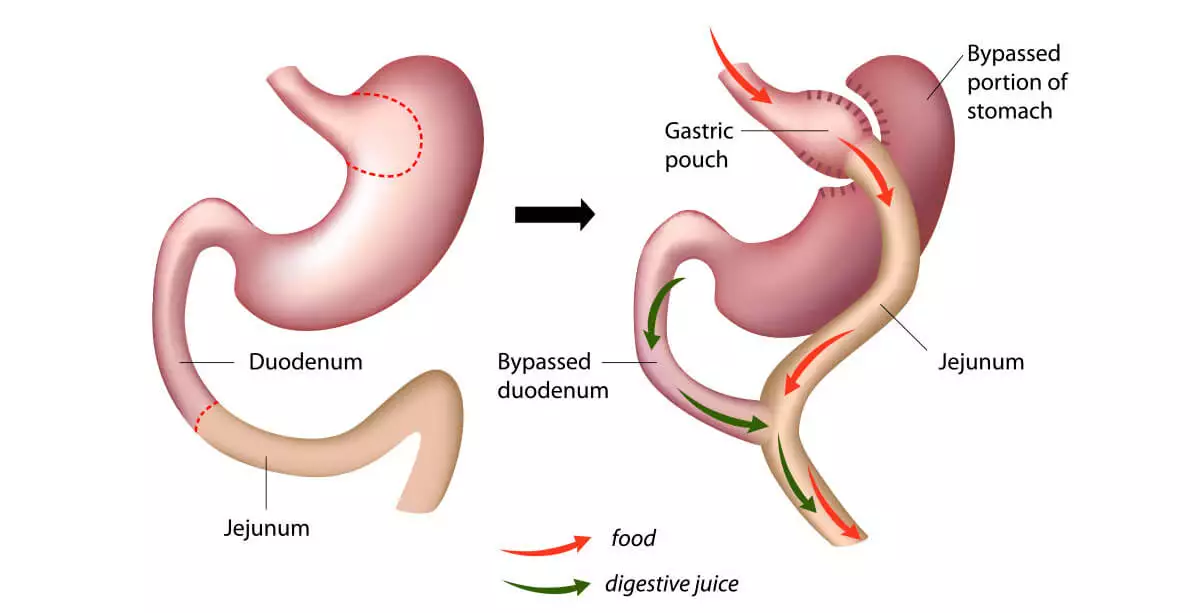
Gastric Bypass surgery, also known as Roux En Y Bypass and Full Gastric Bypass, is one of the most popular Bariatric Surgeries. Gastric Bypass aims to trigger weight loss through modifications to the digestive system that restrict the absorption of the nutrients. The stomach is made smaller, and the effective bowels are shortened.
Gastric Bypass is recommended to patients who are obese and can not lose weight with diet and exercise. Gastric Bypass is also recommended to patients that wish to go through a Bariatric Surgery but suffer from acid reflux caused by hiatal hernias.
After Gastric Bypass, the swallowed food will go into a remodeled small pouch of the stomach and then directly into the intestine, thereby bypassing most of the stomach and the first 4.9 to 6.6 feet (150 - 200 cm) of the small intestine.
The Roux En Y procedure is named after the changes made to the digestive system during it. Roux En Y means in the shape of Y. The procedure divides the stomach and the small intestine, connecting each new segment together to form a Y shape.
Why is Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery Performed?
Obesity has become a pandemic over the last few decades and has substantially lowered the life expectancy and quality of many. Gastric Bypass is used to treat obesity and obesity-related medical conditions. Gastric Bypass alleviates gastroesophageal reflux, heart diseases, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, sleep apnea, and type 2 diabetes. Gastric Bypass does not just treat these conditions by weight loss, but through the lasting modifications made to the digestive system.
Surgical methods, like Gastric Bypass, are often recommended if the patient is morbidly obese to such a degree that even dieting and exercises are not enough to help the patient lose weight.
Gastric Bypass, like Gastric Sleeve, is performed laparoscopically, i.e. using small keyholes instead of opening up the abdomen.
What are The Conditions Of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
The requirements of Gastric Bypass are similar to that of Gastric Sleeve. The final decision on if a patient qualifies for Gastric Bypass or if Gastric Bypass is recommended is made by our Bariatric Team, here are some of the qualifying criteria that our Bariatric Team uses for Gastric Sleeve:
- A Body Mass Index, BMI, of at least 35 is required, or having an obesity related condition with a BMI of 30.
- Must not have tested positive for Covid within the month before surgery.
- Must not have stomach Polyps.
- Must not have an active infection at the time of the surgery.
- Chronic diseases, such as thyroid diseases, Crohn's disease, diabetes, etc, might require additional testing before arriving in Turkey.
- Currently having or having a history of a disease might require a letter of eligibility from the patient’s doctor or require additional consultations after arriving in Turkey.
What Are The Things To Be Considered Before Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
After a patient qualifies for Gastric Bypass, their Patient Coordinator, along with a treatment schedule, will provide the patient with a Liver Fat Reducing Diet that has to be followed before arriving at the hospital. The patient should not consume any food or liquid 12 hours before the surgery. The following dietary and medicinal restrictions have to be followed before the surgery as well:
- Usage of vitamin K should be stopped 30 days before surgery as it is an anticoagulant, i.e. blood thinner, and increases the rate of complications associated with internal bleeding.
- Oral contraceptives and any other contraceptives that have estrogen or progesterone, like coils, HRT patches, or birth control implants, must be stopped or taken off 30 days before the surgery as they increase the rate of complications arising from blood clots. Hormonal and oral contraceptives can be used 30 days after surgery. Non-hormonal implants are safe and recommended if considering a Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y).
- Smoking should be avoided starting a week before surgery until three weeks after surgery. Smoking causes the veins to constrict and limits blood circulation, potentially causing complications such as leakage.
- Alcohol consumption should preferably be avoided in the last 3 months leading up to the surgery. Alcohol consumption a week before surgery should especially be avoided as it will increase the burden on the liver and might cause complications with anesthesia.
- The patient will have a consultation with an internal diseases specialist, radiologist, anesthesiologist, and a general surgeon before the surgery.
- Preoperative tests at the hospital will include full abdominal ultrasound, chest x-ray, breath functioning test, electrocardiogram, endoscopic investigation of the stomach, and full blood test as pre operation test and exams.
What Are The Things To Be Considered During Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes 4 - 6 small cuts on certain points of the patient's abdomen. These help to insert the scope and needed instruments that will be used to perform the surgery.
A camera is inserted into the patient that is connected to a video monitor in the surgery room, the camera allows the surgeon to view the inside of the abdomen while operating.
The surgeon divides the stomach into a small upper pouch and a larger bottom section by using staples. Ingested food will go through the upper pouch, and the pouch has enough volume to hold about an ounce, around 28 grams, of food.
The surgeon then connects the Jejunum to the pouch. The food then passes from the small pouch to the new opening and into the small intestine causing the body to absorb less calories.
The surgeon, then, uses the stapler to divide the upper part of the small intestine into a tube with two ends. One end of the small intestine, the Roux limb, is brought up to the stomach pouch, and a small connection, an anastomosis, is made between them.
The other end of the small intestine is then connected to another part of the small intestine. At the end the surgeon may test for leaks with a dye study or an upper endoscopy.
Note that the unused parts of the stomach, unlike the Gastric Sleeve, are not removed.
Laparoscopic Gastric bypass surgery takes around 2-3 hours.
What Are The Things To Be Considered After Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
Gastric Bypass prescriptions given to the patients after the operation will include blood thinner injections and stomach protectors. The medicine provided will include antibiotics and painkillers that should be used if needed. Booking Surgery dieticians will provide a diet list for each patient and will provide additional support if needed. The initial dietary restrictions post surgery will be as follows:
- The patients will only consume liquids for the first 3 weeks following surgery. Also called the liquid stage, patients are advised to consume protein shakes, soups, herbal tea, etc.
- The patients are advised to consume puree and liquid foods for the following 3 weeks. Also called the puree stage, patients are recommended to increase their diet by eating mash and blended foods.
- After 6 weeks of liquid and puree stage, the patients can start consuming solid foods. After Gastric Bypass surgery, patients should never eat solid and liquid foods at the same time.
- Additionally, patients should avoid caffeinated or carbonated drinks for 2 months following surgery, but decaffeinated coffee can be safely consumed 10 days after surgery.
- Patients should also avoid smoking, alcohol, and any recreational drugs for at least 3 weeks following surgery.
Post surgery, some physical activities should be avoided as well:
- Patients can go back to work 2 weeks after getting home if it's not a physically strenuous job.
- Patients should avoid strenuous activity and sexual intercourse for the first month following surgery.
- Patients should walk frequently and should not do any heavy lifting more than 5 KG for the first month following surgery and not more than 10 KG for the first 3 months after surgery.
- Patients can start exercising to help the weight loss process 2 months after the surgery.
Additionally, the surgical stitches will dissolve on their own, but if they do not, patients should take an appointment from their GP to get them removed.
What are the Short-term Risks of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
Gastric Bypass Surgery, while considered relatively safe mainly due to it being done Laporoscipally, has some risks associated with it like any major surgery. These risk include:
- Bleeding
- Infections
- Intestinal Obstruction
- Leakage
- General anesthesia complications
- Blood clots
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
Blood thinners and compression socks provided after surgery lower the likelihood of blood clots and deep vein thrombosis.
These risks most likely show up within the first month after surgery.
What are the Long-term Complications of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
The long-term complications of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery can be explained as follows:
Malnutrition:
Malnutrition occurs when the body is deprived of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients needed to maintain healthy tissue and organ function.
The long term side effects of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery, as a result of malnutrition, include:
- Vomiting
- Pain
- Fatigue
- Dry Skin
- Mood Changes
- Hair Loss
- Hernias
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Hypoglycemia
Gallstones:
During the rapid weight loss after Gastric Bypass surgery, approximately the first 6 months, gallstone formation increases by up to 20%.
Dumping syndrome:
Dumping syndrome is caused by the food and liquids in the stomach reaching the small intestine in a short time after gastric Bypass Surgery.
What To Do When Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery Doesn't Work?
If the Roux En Y Gastric Bypass surgery is performed correctly by a certified surgeon, it has a very small risk of failure. The surgery is considered a failure if the patient regains the weight in a few years. Going back to old eating habits by forcibly overeating or frequently drinking carbonated drinks may cause the stomach to enlarge, therefore allowing weight regain.
Poor weight loss often leads to consideration of a revision surgery. In such a case, a revision from gastric bypass to gastric bypass might be performed by reducing the size of the dilated pouch or narrowing the Bypass surgery’s anastomosis.
What Are the Advantages Of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) is one of the most commonly performed types of bariatric surgery. The advantages of gastric bypass, which is considered the golden option for bariatric surgeries, can be listed as follows:
- Gastric Bypass is reversible as parts of the old stomach are not removed from the abdomen.
- Alleviates obesity-related health problems such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and acid reflux.
- Within the first year after the surgery, patients lose 75% of their excess body weight, and 80% - 90% of their excess body weight within the first two years.
- Less likely to gain back excess weight, unlike yo-yo dieting, the weight loss is usually for life.
- Produces positive changes in intestinal hormones that reduce appetite and increase the feeling of fullness.
- Decrease in excess weight alleviates the pressure on the knees and joints, increasing the recovery rate of osteoarthritis up to 85%.
What Are the Disadvantages of Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y) Surgery?
While Gastric bypass surgery has many advantages, it does possess some disadvantages that have to be considered before going through with the surgery. Some of the disadvantages include:
- Fewer options when revision surgery is required.
- Compared to other stomach reduction operations, the possibility of complications is higher since the operation involves a wider portion of the digestive system.
- Although it is rare, as Gastric Bypass reduces absorption, vitamin deficiency may occur.
- Bariatric vitamin supplements have to be taken permanently after the operation.
- Endoscopy becomes harder to perform on the patient after the Gastric Bypass, but is still possible.
How much weight can you lose with gastric bypass surgery?
The patients, on average, lose 80% of their excess body weight within a year, their weight loss slows down afterward and stabilizes near their target weight.
The rate and amount of weight loss vary greatly from person to person, and according to lifestyle choices and eating habits of the patient as well as their gender and age.
How painful is gastric bypass surgery?
Like the Gastric Sleeve Surgery, the patient is under general anesthesia during the Gastric Bypass Surgery, so there is no pain during the procedure. Gastric Bypass has a comfortable healing process as the surgery is performed laparoscopically with only a few keyhole incisions. Painkillers are provided to prevent any pain after surgery as well. Gas pain occurs due to the modifications made to the digestive system, and patients are encouraged to start walking just 4 hours after the surgery to combat the gas pain
How long does gastric bypass surgery take?
The operation, on average, takes 1.5 - 2 hours. Aiming to provide a robust post operative experience, total hospital stay is around 5 days where the patient remains under surveillance in a fully equipped hospital room until discharge. Booking Surgery provides full hospital stays for each Bariatric Surgery to prevent possible complications.
Who can have gastric bypass surgery?
Gastric Bypass provides the same advantages for obesity related conditions as Gastric Sleeve Surgery. While Sleeve Gastrectomy exacerbates Acid Reflux, Gastric Bypass eliminates all symptoms of Acid Reflux. But, Sleeve Gastrectomy does not modify the intestines, is a simpler and shorter procedure, and does not complicate future colonoscopies. Both surgeries have pros and cons that make them unique, they offer a trade off between complexity and effectiveness. Neither is better than the other, and the Bariatric Surgeon recommendation should be followed.
Which is better: Roux-en-Y or Gastric Sleeve?
Different criteria are evaluated to ensure that gastric bypass surgery is an appropriate procedure for the patient. Patient’s medical history, body mass index, and personal weight loss goals are important factors in determining whether they are a suitable candidate for Gastric Bypass. If the patient suffers from Acid Reflux, the most appropriate bariatric operation is Gastric Bypass, because Acid Reflux is greatly alleviated after Gastric Bypass Surgery. Patients have to have a Body Mass Index, BMI, higher than 30 or must be suffering from obesity related conditions to meet the eligibility criteria.
What are possible side effects of the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass?
- Vitamin and Mineral Deficiency
- Hair loss: Hair loss is due to weight loss experienced after obesity surgeries. Vitamins such as Biotin alleviate it to a degree.
- Bleeding
- Infections
- Intestinal Obstruction
- Leakage
- General anesthesia complications
- Blood clots
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
Can you gain weight after the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass?
As with other bariatric surgery methods, there is no guarantee that weight loss will be permanent after Gastric Bypass Surgery. Having an active lifestyle, and keeping a healthy diet will make weight regain less likely.
Is Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass permanent?
Gastric Bypass Surgery, without medical intervention, is permanent. And if the patient has a habit of eating healthy and staying away from foods and drinks that will enlarge their stomach,the weight loss is permanent as well. Gastric Bypass, if needed, can be reversed through a laparoscopic procedure.
How long do you stay in the hospital after the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass?
Total hospital stay is around 5 days, 4 days of which are after the surgery. Booking Surgery aims to provide a robust post operative experience while the patient remains under surveillance in a fully equipped hospital room until discharge, therefore providing a full hospital stay to prevent possible complications.
Is the stomach removed in the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass?
Roux En Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) surgery technique involves the creation of a new stomach with a volume of 15 - 30 cc, the old stomach is kept passive and does not assist with digestion. Since the old stomach is still present in the body, Roux En Y Gastric Bypass does not remove the stomach.
What is Body Mass Index (BMI)?
Body mass index (BMI) or height-weight index is a calculation method that shows the estimated fat content of a person's body. This method is based on the person's height to weight ratio. According to the result of the index, the proximity and distance of the person's current weight to his/her ideal weight can be calculated
How is Body Mass Index Calculated?
Body mass index is calculated by dividing the body weight by the square of the height (kg/m⊃2;).
Results below 18.5 kg/m⊃2;: Below ideal weight
Results between 18.5 kg/m⊃2; and 24.9 kg/m⊃2;: Ideal weight
Results between 25 kg/m⊃2; and 29, 9 kg/m⊃2;: Above ideal weight
Results between 30 kg/m⊃2; and 39, 9 kg/m⊃2;: Above ideal weight (obese)
Results above 40 kg/m⊃2;: Above ideal weight (morbidly obese)
What Do Body Mass Index Results Mean?
Body mass index calculation does not include factors such as fat ratio, body type, fat and muscle tissue. For this reason, experts obtain more detailed information about the person's weight problem by measuring the metabolic rate and detailed body analysis, in addition to measuring the body mass index and waist circumference in calculating the ideal weight. The fact that the person is above or below the ideal weight should be evaluated by the physician together with other factors. Action should be taken together with the physician to eliminate existing health problems and prevent possible health problems.
In men, if the waist circumference exceeds 94 cm, it is considered an increased risk, and if it exceeds 102 cm, it is considered high risk. In women, this ratio is considered increased risk if it exceeds 80 cm and high risk if it exceeds 88 cm.
Obesity Calculation with Detailed Body Mass Index
In calculating obesity with detailed body mass index, it can be learned whether the weight, body fat percentage and waist circumference are within normal values, taking into account age and gender.
First of all, it is very important for the diagnosis and treatment of obesity to know where the fat tissue accumulates in the body. The way fat tissue accumulates in the body can be divided into two as apple type and pear type.
In apple type obesity, fat accumulates around the belly. In pear type obesity, it is observed to accumulate in the hips and thighs. However, the fat accumulated around the navel is considered to be more dangerous and has a higher risk of heart disease than the fat accumulated in the hips and thighs.
